Our eyes can both see far and near because they have the ability to focus "similar to a camera, based on the distance of objects". The human eye has the ability to automatically change its refractive power, enabling light from different distances to form a focus on the retina and thus allowing for a clear view of targets at various distances. The process by which the human eye changes the magnitude of the refractive power of the eye's refractive system (adjusting the focal length) is called adjustment. If the eye is compared to a camera, the eye's adjustment function is like the camera's zoom. The refractive system of the eye (cornea, aqueous humor, and lens) is equivalent to the zoom lens of a camera, the pupil is equivalent to the aperture of a camera, and the retina is equivalent to the film of a camera for imaging.
The influence of regulatory function on visio
When children read books, do homework, look at electronic products, play the piano, play with Lego, build with blocks, draw pictures and so on for a long time, it all belongs to long-term close-range eye use. This will cause the ciliary muscle to remain in a contracted state all the time, leading to "ciliary muscle spasm". Over time, it will result in a decrease in accommodation sensitivity and insufficient accommodation. When the accommodation power is insufficient, the eye cannot focus the image behind the retina onto the retina, which may lead to a hyperopic defocus state, causing the choroid to become thinner and the eye axis to elongate, resulting in rapid progression of myopia.
How to improve and enhance the regulatory functionIt is necessary to confirm whether the child's refractive error status has been properly corrected. For instance, if a child has problems such as myopia, hyperopia or astigmatism but does not get glasses fitted or the prescription is inappropriate, all these can lead to adjustment issues. Therefore, getting glasses scientifically is the top priority. Adjustment training is also required, such as reverse racket training. Additional reading mirror, front mirror additional. For patients with insufficient accommodation or accommodation paralysis caused by some lesions, long-term orthoscopy supplementation is required.
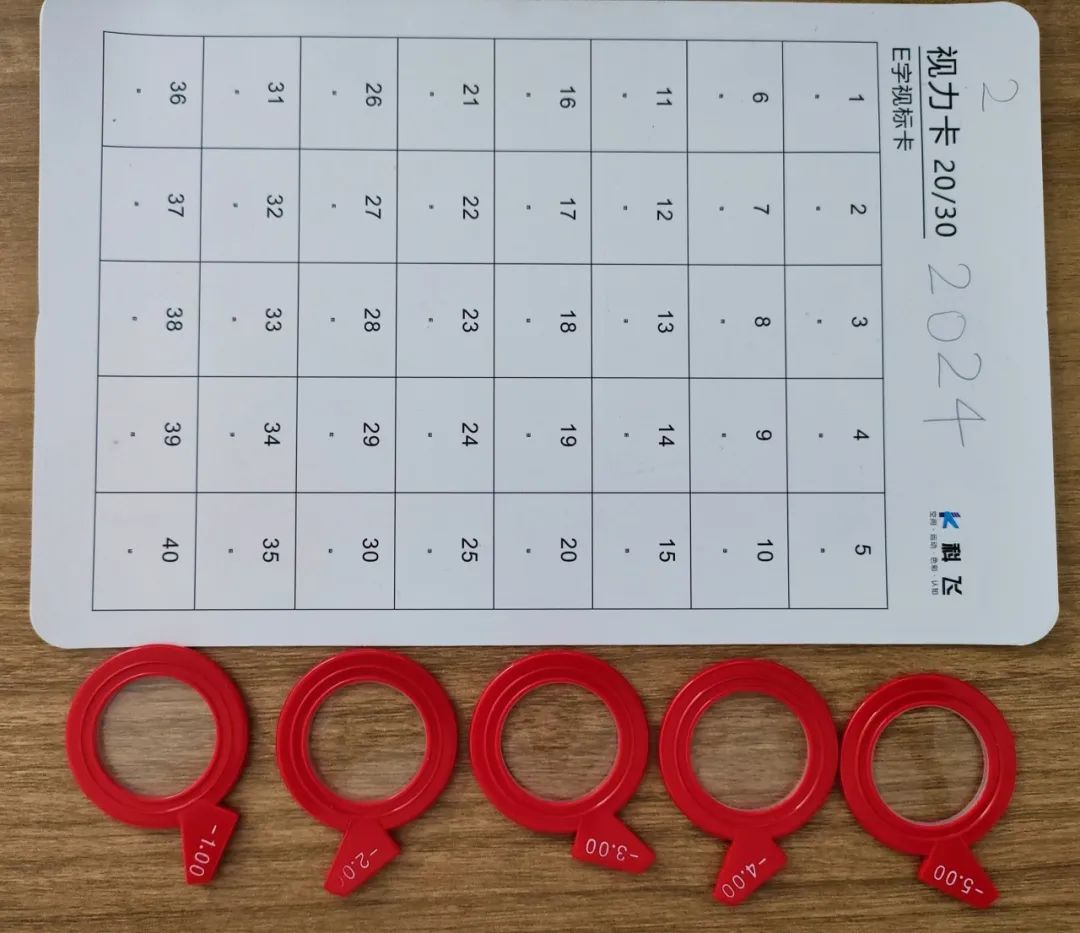

When training, the first step is to correct refractive errors. The training method can adopt lens reading (first conduct frontal lens reading), and at the same time combine it with the training of the dispersion function. Visual training: Reverse shooting or close-range use of additional lenses.
The patient's accommodative sensitivity and accommodative amplitude were trained by having them alternately gaze at two visual acuity charts, one far and the other near. This method is helpful in improving the patient's ability to adjust and switch between near and far vision.
